Explain Fully Null Hypothesis Sampling Difference and Significant Difference
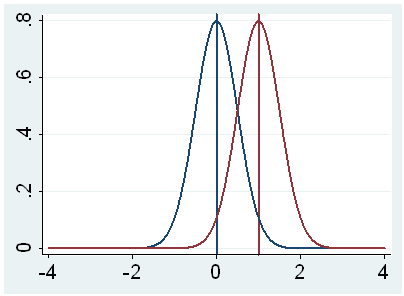
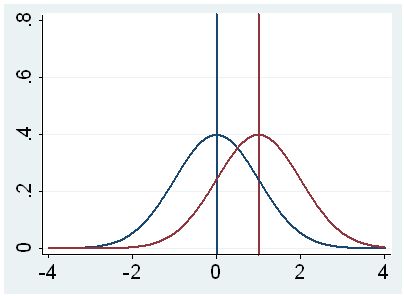
The true difference in height is NOT equal to 0 in the population. As we saw in the three examples the null hypothesis suggests nothing special is going on.

Hypothesis Test For Difference Of Means Video Khan Academy
A confidence level of 95 percent or 99 percent is common.

. Similarly when we do a correlation the null hypothesis is normally implicitly r0 but you could make your null that a. The difference between the means is statistically significant at the 05 level t2333 df11 Should you conclude that the null hypothesis has been rejected. One interpretation is called the null hypothesis often symbolized H 0 and read as H-naught.
When your p-value is less than or equal to your significance level you reject the null hypothesis. In hypothesis testing Claim 1 is called the null hypothesis denoted Ho and Claim 2 plays the role of the alternative hypothesis denoted Ha. It is one of two mutually exclusive hypotheses about a population in a hypothesis test.
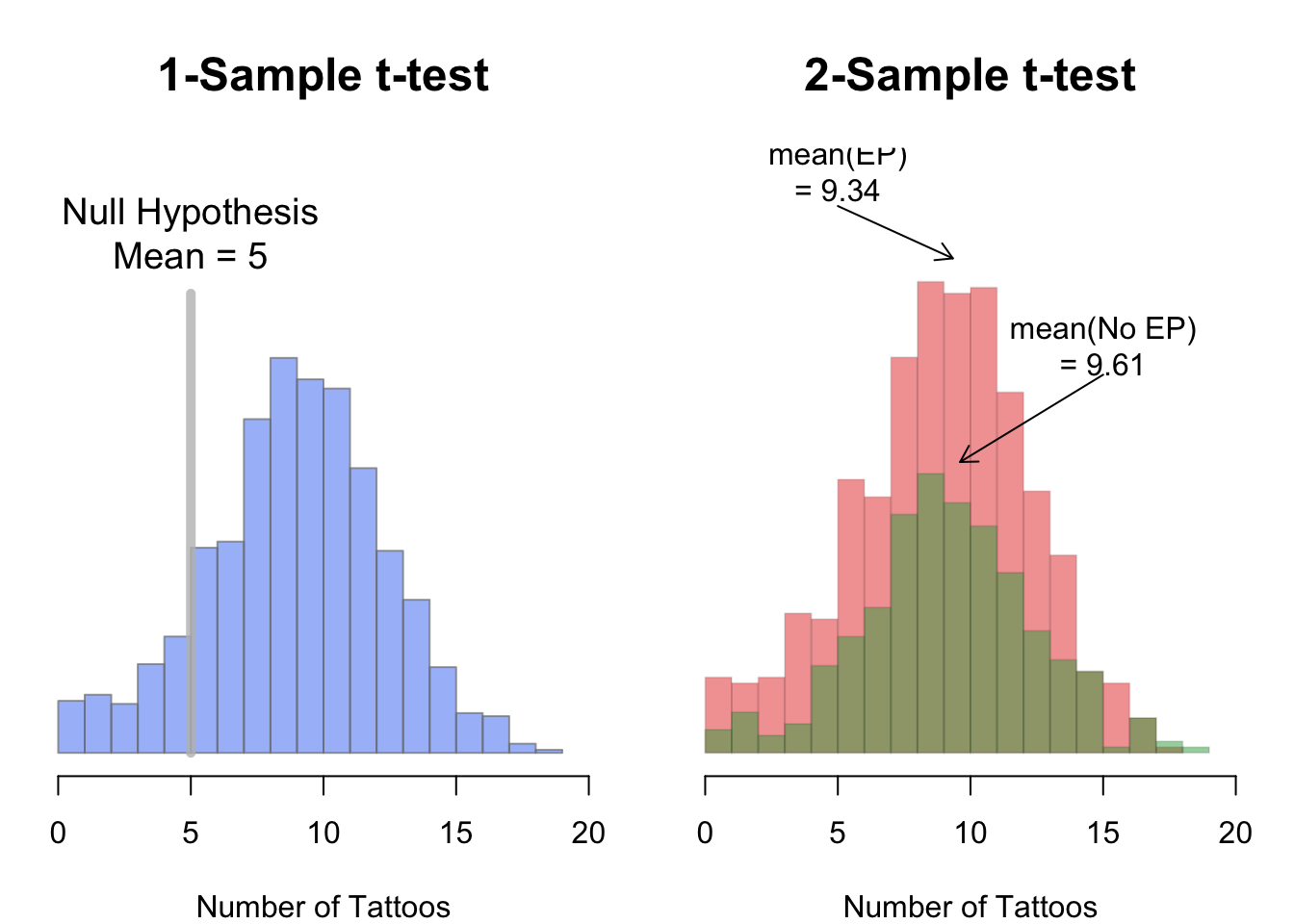
The null hypothesis would be that both theres no difference between the sample mean and the population mean. In other words there is no change from the status quo no difference from the traditional state. Hypothesis Testing Santorico - Page 271 There are two types of statistical hypotheses.
Should the null hypothesis for Immigrated to the United States be rejected. They sample 100 first-time borrowers and find 53 of these loans are smaller that the other borrowers. Read the research question.
Set the null and alternative hypothesis. When your sample contains sufficient evidence you can reject the null and conclude that the effect is statistically significant. The null hypothesis is also known as the H 0 or no-difference hypothesis.
Your results are not significant. The data favors the alternative hypothesis. Explain the basis for your answer.
Suppose you read this statement. The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Verify that we have a single sample that addresses a binomial proportion.
á 005 is merely a convention that evolved from the practice of RA. The method developed by Fisher 1934. To distinguish it from other hypotheses the null hypothesis is written as H0 which is read as H-nought H-null or H-zero.
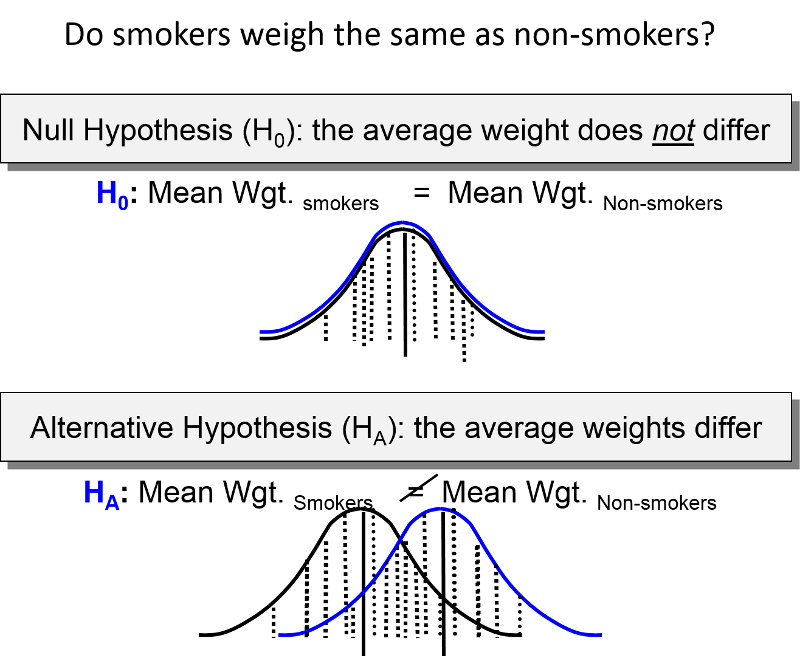
In an experiment the alternate hypothesis suggests that the experimental or independent variable has an effect on the dependent variable. Explain fully cross-tabulation and give an example. The null hypothesis in statistics states that there is no difference between groups or no relationship between variables.
The alternate hypothesis H A or H 1 proposes that observations are influenced by a non-random factor. When your p-value is greater than your significance level you fail to reject the null hypothesis. PrF is the p-value of the F statistic and shows how likely it is that the F-value calculated from the F-test would have occurred if the null hypothesis of no difference was true.
Fisher 1959 allows to compute the probability of observing a result at least as extreme as a test statistic eg. A significance test is used to determine the likelihood that the results supporting the null hypothesis are not due to chance. The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
There is convincing evidence to support the claim that the proportion of times she needs to stop at the crossing is the same for the different routesMy AwnserB The pp-value. There is no sharp distinction between significant and not significant results only. Fisher significance testing and the p-value.
Your results are statistically significant. Null hypotheses do not need to be about 0 just about 0 difference. Assume now we are testing our research hypothesis of eg d05 as meaningful non-nil null hypothesis d_0 since we are hard-boned falsificationists.
Review the research question and identify the null hypothesis. Null hypothesis testing is a formal approach to deciding between two interpretations of a statistical relationship in a sample. Then the probabilty to identify a possibly correct alternative d_1 which actually is Power right will be higher the larger the difference between d_0 and.
The alternative is h1. Yes the Null Hypothesis should be rejected. T value assuming the null hypothesis of no effect is trueThis probability or p-value reflects 1 the conditional probability of achieving the observed outcome.
When you fail to reject null hypothesis it means there is insufficient evidence to reject The use of á 005 is a standard with an objective basis No. Should the null hypothesis for Immigrated to the United States be rejected. Failure to reject null hypothesis leads to its acceptance.
A non-directional or two tailed hypothesis simply states that there will be a difference between the two groupsconditions but does not say which will be. They perform a hypothesis test to determine if the percentage is the same or different from 50. Null Hypothesis H0 a statistical hypothesis that states that there is no difference between a parameter and a specific value or that there is no difference between two parameters.
Explain the basis for your answer. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors. You can imagine the first hypothesis called null-hypothesis as a kind of default in significance testing that is probably the most confusing thing at first.
The directional hypothesis can also state a negative correlation eg. The null hypothesis H0 implies that there is no significant difference between the averagesmeans of the two sets of sample. The weighted sample would be the sample if you were evaluating the mean height of a basketball team vs the general population.
For the hypothesis test they choose a 5 level of significance. Is the difference for Some college statistically significant. Identify the value of binomial parameter p when there is truly no difference Write the null hypothesis in this form.
The pp-value is greater than αα and the null hypothesis is not rejected. From this output we can see that both fertilizer type and planting density explain a significant amount of variation in average crop yield p-values 0001. Explain the basis for your answer.
Explain fully null hypothesis sampling difference and significant difference. The alternative hypothesis H1 implies that there is a significant difference between the averagesmeans two populations and that this variation is improbable to have been contributed due to sampling error. This is the idea that there is no relationship in the population and that the relationship in the sample reflects only.
The higher the number of face-book friends the lower the life satisfaction score. Explain fully what is meant by a relationship and the 4 types of relationships between 2 variables. The alternate would be that the sample mean is greater than the population mean.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HypothesisTestinginFinance1_2-1030333b070c450c964e82c33c937878.png)
Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples

Hypothesis Testing For Means Proportions

Interpret The Key Results For 2 Sample T Minitab Express
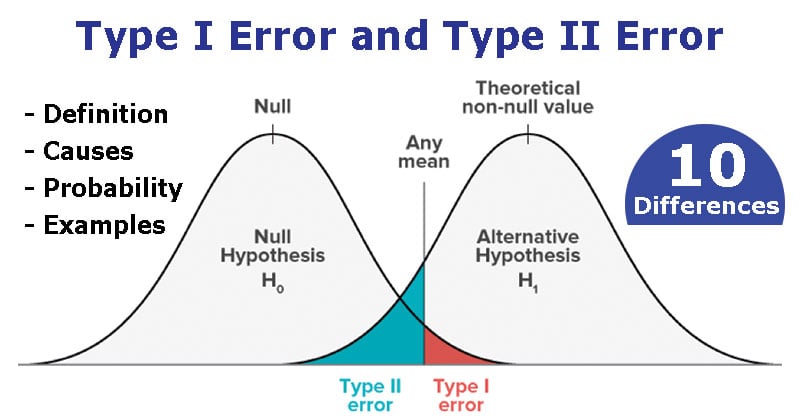
Type I Error And Type Ii Error Definition 10 Differences Examples Microbe Notes
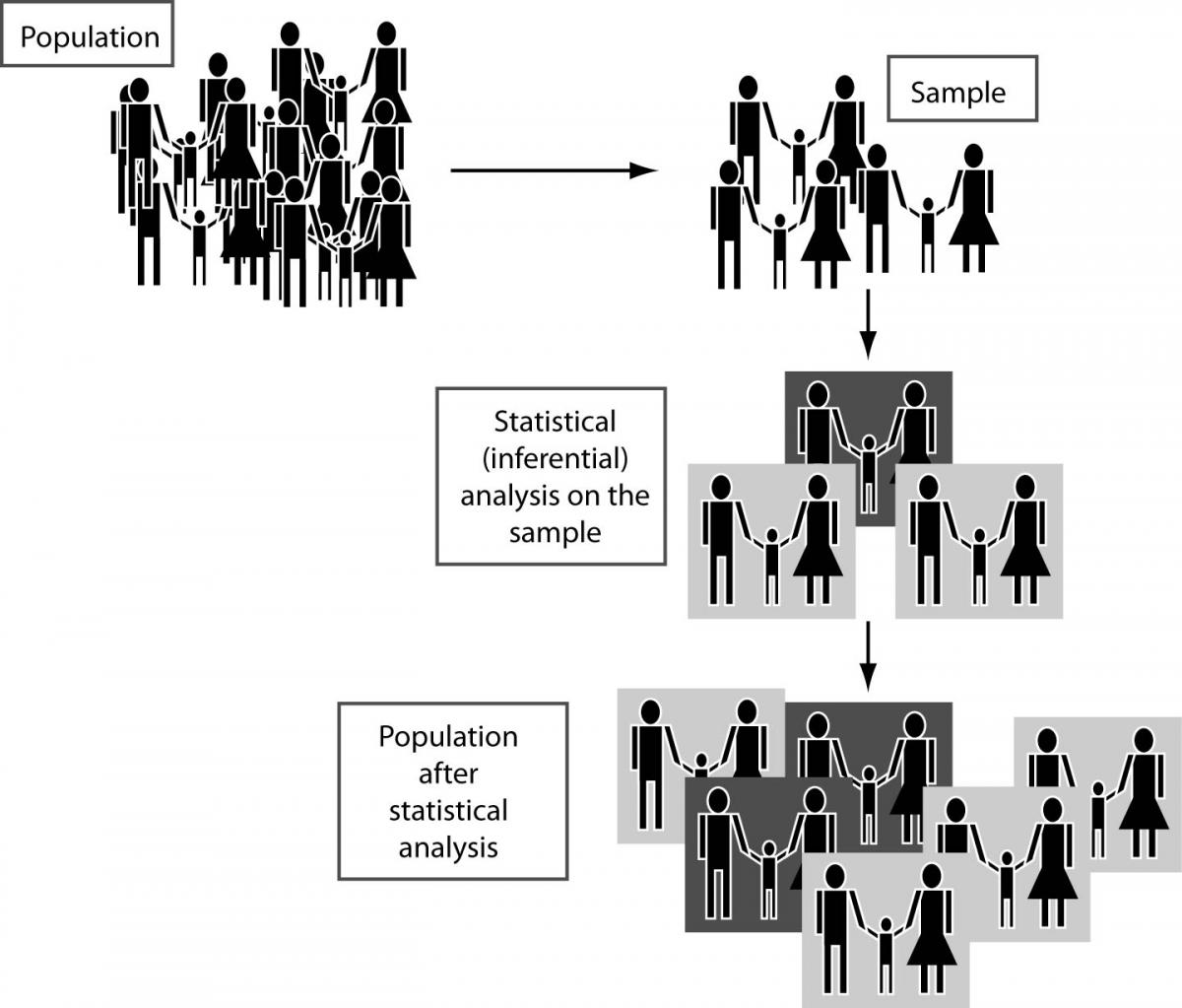
Comparing Groups For Statistical Differences How To Choose The Right Statistical Test Biochemia Medica

An Absolute Guide On The Significance In Statistics Statistics Math Maths Algebra Formulas Statistics

Parameter Vs Statistic When To Use Statistic Vs Parameter With Useful Examples 7esl Data Science Learning Confusing Words Statistics Math

Hypothesis Testing Ii The Two Sample Case Ppt Download

Example Of Hypotheses For Paired And Two Sample T Tests Video Khan Academy

Using Confidence Intervals To Compare Means Statistics By Jim
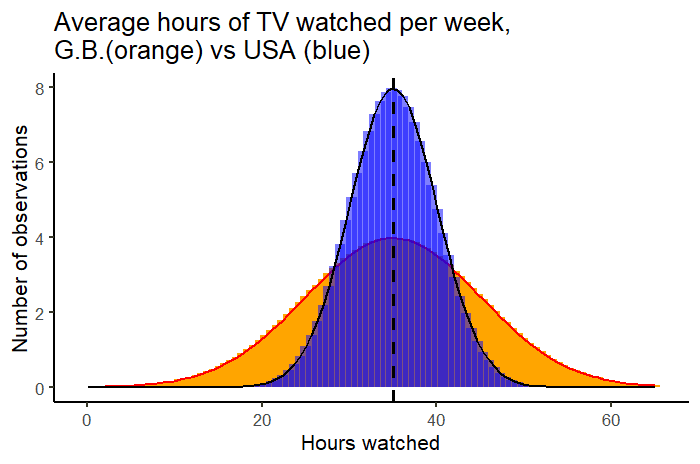
Understanding Confidence Intervals Easy Examples Formulas
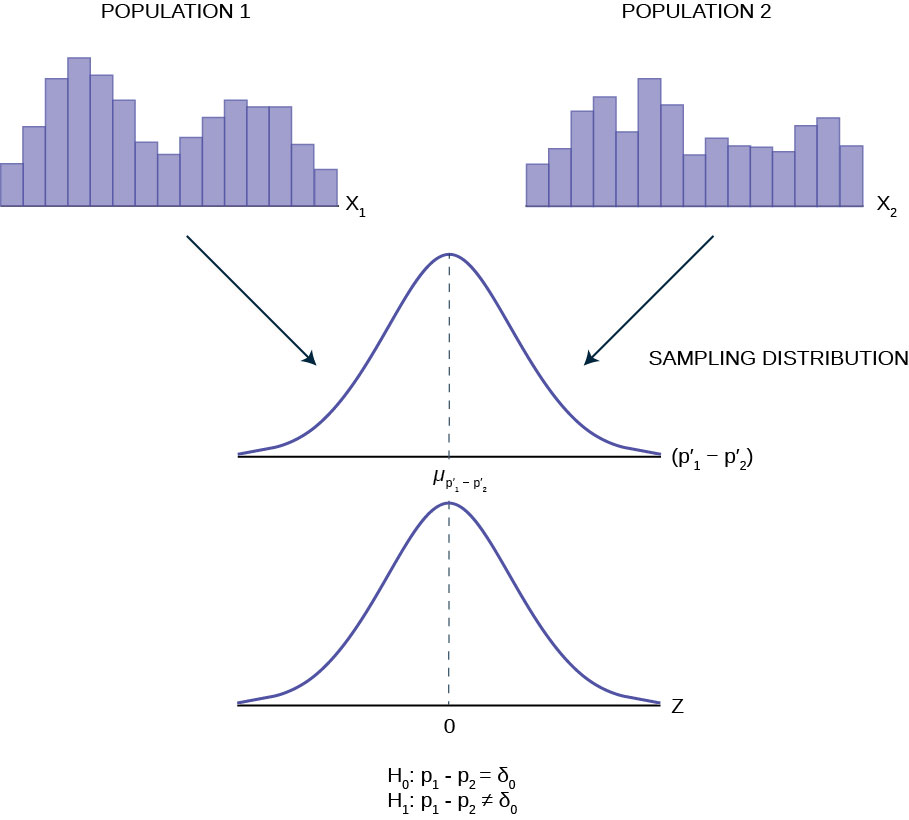
Comparing Two Independent Population Proportions Introductory Business Statistics
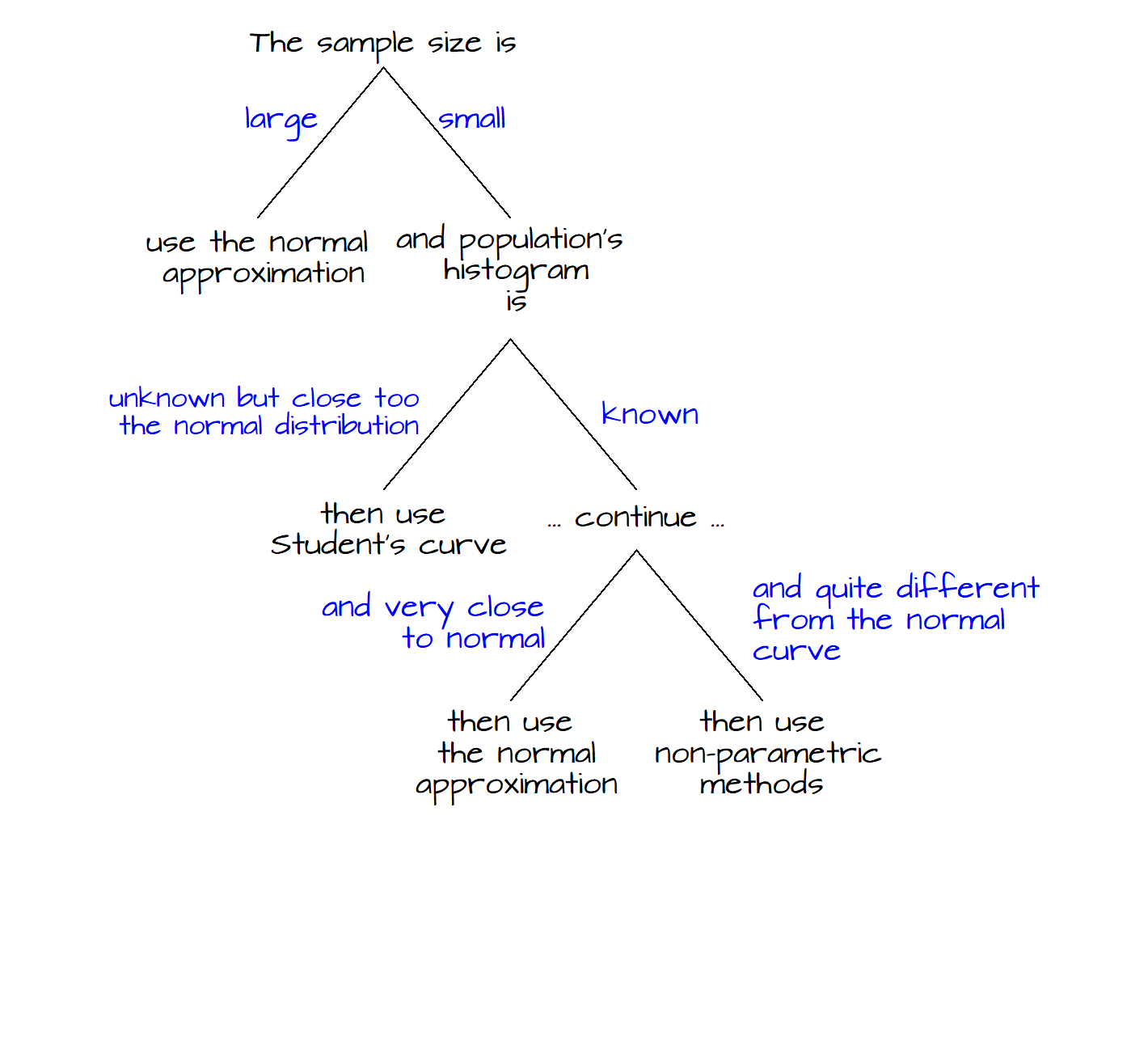
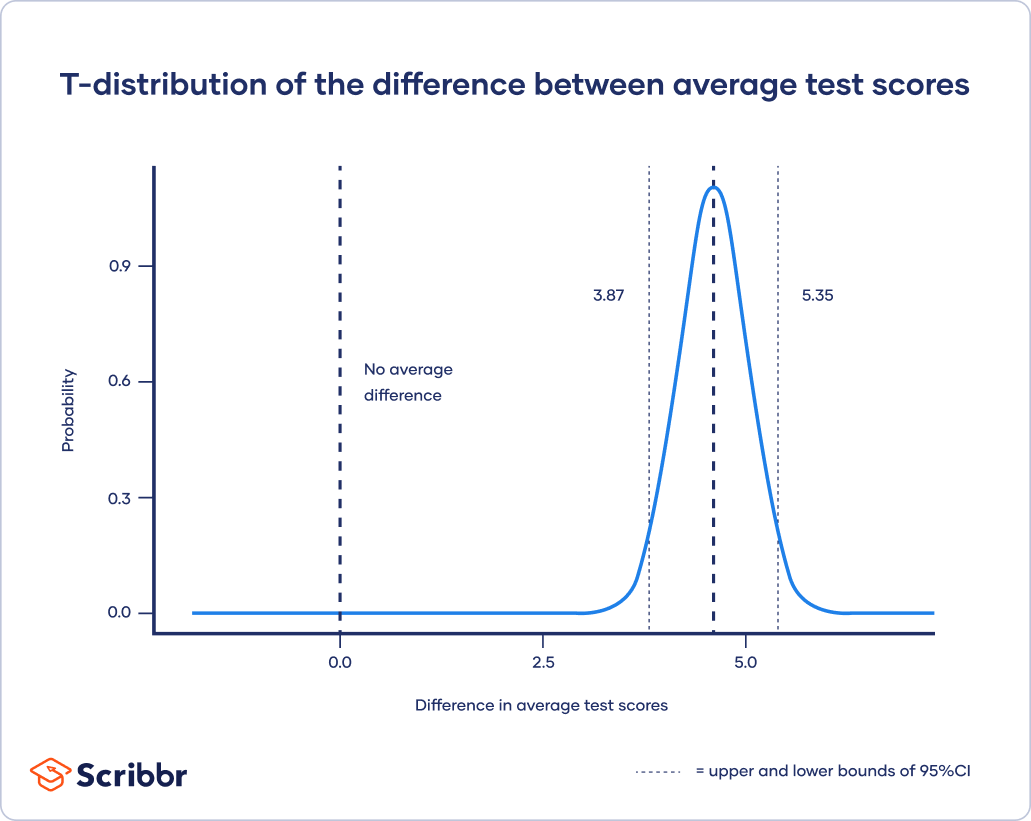

Comments
Post a Comment